Product Description
Product Description
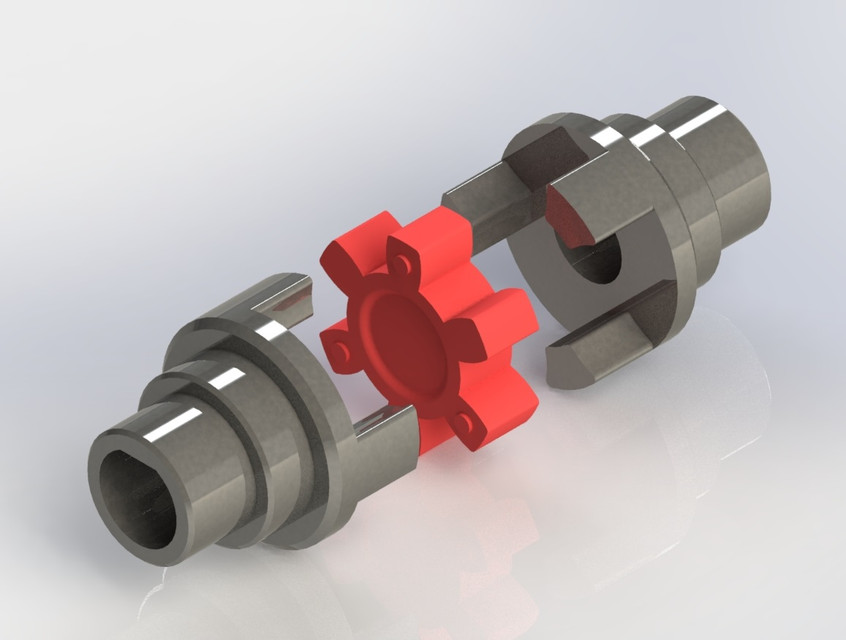
Coupling Deatails
Name: High precision plum blossom
coupling Model: LM-Material: Aviation Aluminum Alloy
Working temperature: -40 ° C ~ 100 ° C
Support customization: Factory direct sales support customization.
Features:
1.Intermediate Elastomer Connection-Absorbs vibration, compensates for radial, angular, and axial 2.misalignment
3.Oil resistance and electrical insulation
4.Clockwise and counterclockwise rotation characteristics are identical-there are 3 different hardness 5.elastomer
6.Fixation by clamping screw.
|
Model parameter |
ΦD |
L |
LF |
LP |
F |
M |
Tightening screw torque |
|
(N.M) |
|||||||
|
GF-14X22 |
14 |
22 |
14.3 |
6.6 |
3.8 |
M 3 |
0.7 |
|
GF-20X25 |
20 |
25 |
16.7 |
8.6 |
4 |
M 3 |
0.7 |
|
GF-20X30 |
20 |
30 |
19.25 |
8.6 |
5.3 |
M 4 |
1.7 |
|
GF-25X30 |
25 |
30 |
20.82 |
11.6 |
5.6 |
M 4 |
1.7 |
|
GF-25X34 |
25 |
34 |
22.82 |
11.6 |
5.6 |
M 4 |
1.7 |
|
GF-30X35 |
30 |
35 |
23 |
11.5 |
5.75 |
M 4 |
1.7 |
|
GF-30X40 |
30 |
40 |
25.6 |
11.5 |
10 |
M 4 |
1.7 |
|
GF-40X50 |
40 |
50 |
32.1 |
14.5 |
10 |
M 5 |
4 |
|
GF-40X55 |
40 |
55 |
34.5 |
14.5 |
10 |
M 5 |
4 |
|
GF-40X66 |
40 |
66 |
40 |
14.5 |
12.75 |
M 5 |
4 |
|
GF-55X49 |
55 |
49 |
32 |
16.1 |
13.5 |
M 6 |
8.4 |
|
GF-55X78 |
55 |
78 |
46.4 |
16.1 |
15.5 |
M 6 |
8.4 |
|
GF-65X80 |
65 |
80 |
48.5 |
17.3 |
18.1 |
M 8 |
10.5 |
|
GF-65X90 |
65 |
90 |
53.5 |
17.3 |
18.1 |
M 8 |
10.5 |
Product Parameters
Detailed Photos
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
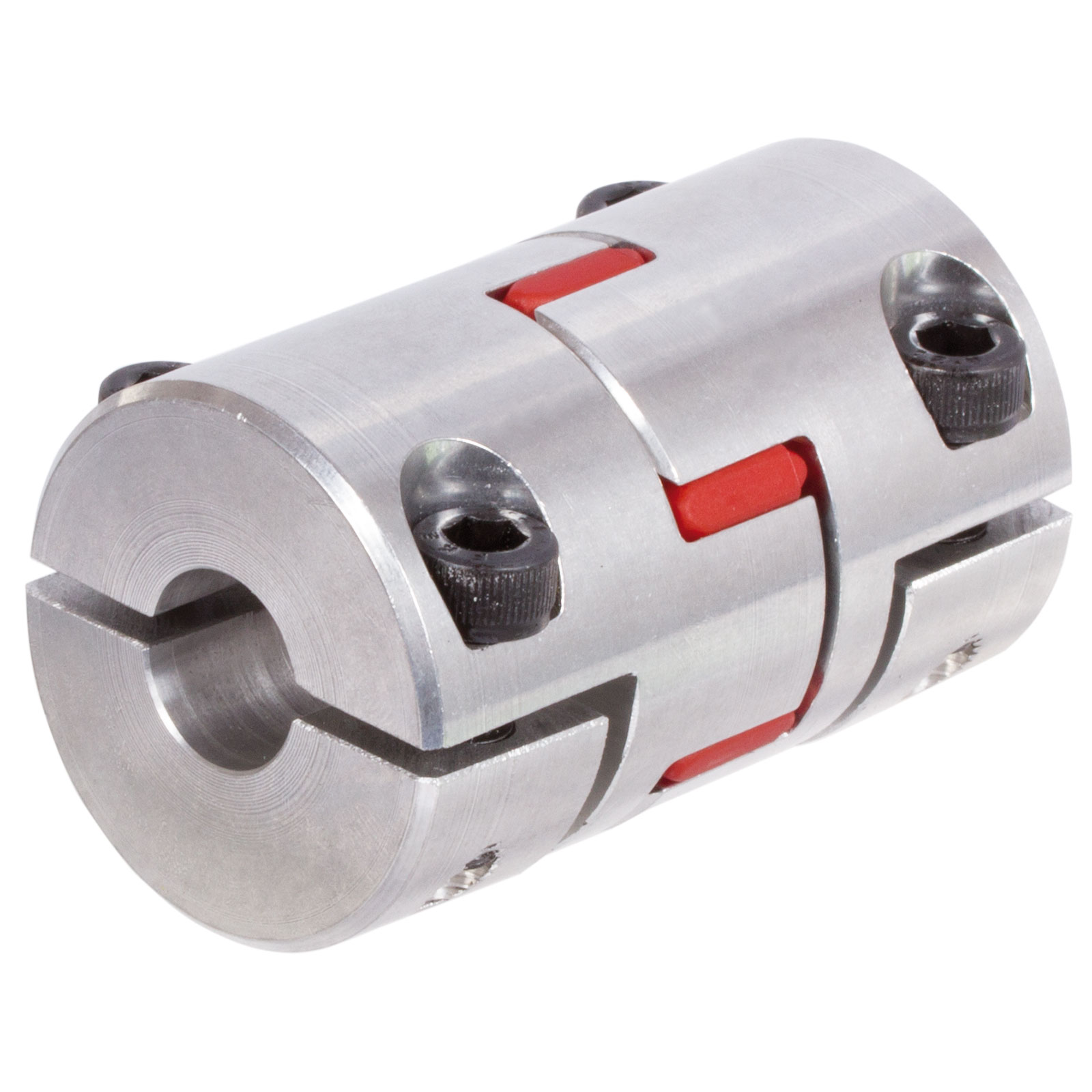

Maintenance Requirements for Optimal Performance of Elastic Couplings
Maintaining elastic couplings is essential to ensure their optimal performance and longevity. Following these maintenance guidelines can help prevent premature wear and failure:
- Regular Inspection: Periodically inspect the coupling for signs of wear, such as cracks, deformities, or visible damage. This can help identify issues early and prevent further damage.
- Lubrication: Some elastic couplings require lubrication to reduce friction and wear. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for lubrication intervals and use compatible lubricants.
- Torque Check: Check the coupling’s torque values to ensure they are within the specified range. This helps maintain proper torque transmission and prevents overloading.
- Alignment Check: Monitor the alignment of the connected shafts regularly. Misalignment can cause excessive stress on the coupling, leading to premature failure.
- Vibration Analysis: Perform vibration analysis to identify any abnormal vibrations in the system. Excessive vibrations could indicate coupling or system issues that need attention.
- Temperature and Environment: Ensure that the coupling operates within the recommended temperature and environmental limits. Extreme conditions can affect the coupling’s material properties and performance.
- Coupling Wear: Keep track of the coupling’s wear over time. Depending on the application, the coupling might need replacement after a certain period of service.
- Expert Inspection: If any unusual symptoms or problems arise, consider having the coupling inspected by a qualified technician or engineer to diagnose the issue accurately.
Adhering to these maintenance practices helps extend the service life of elastic couplings, ensures reliable performance, and minimizes unexpected downtime and costly repairs.
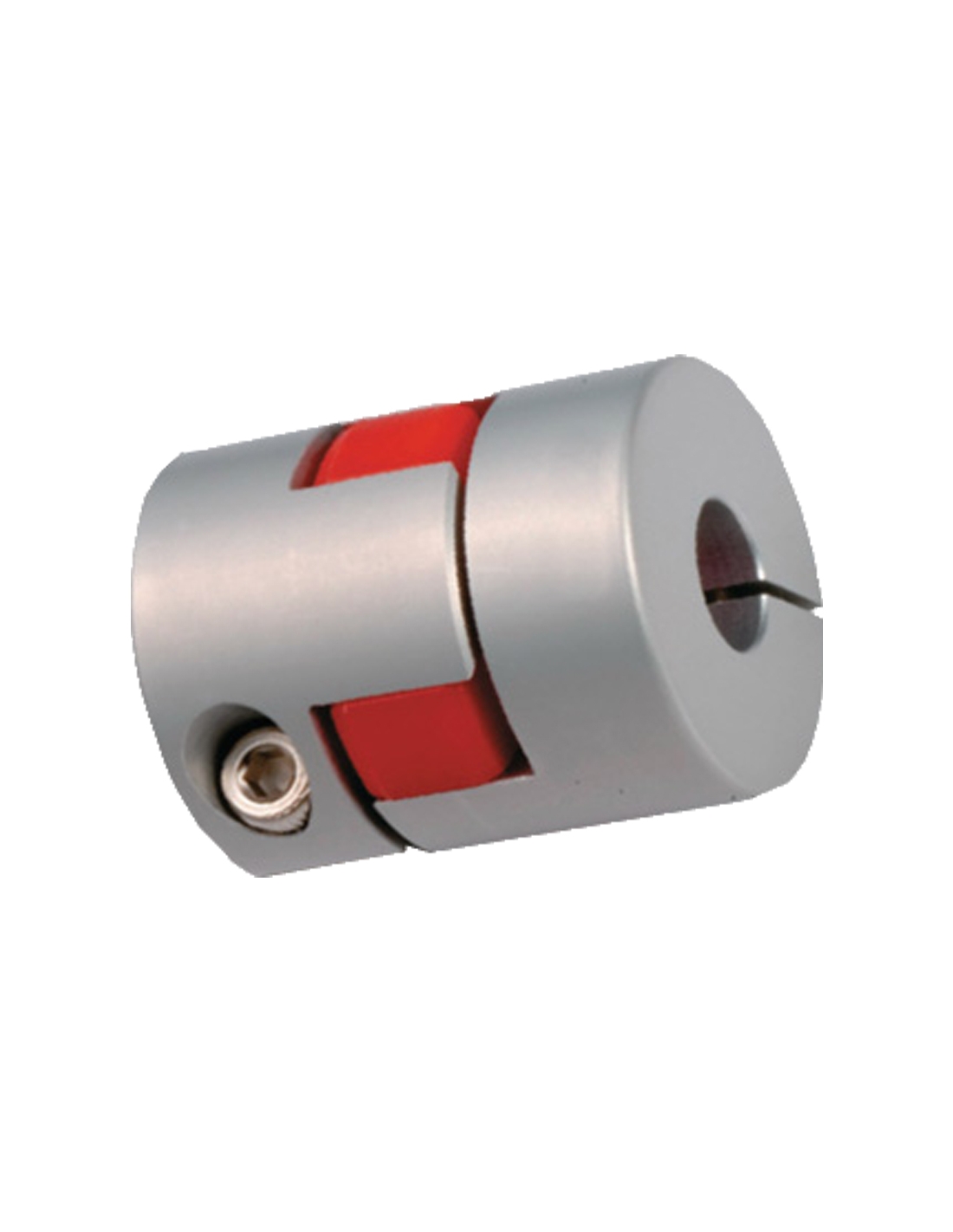

Alternatives to Elastic Couplings for Flexible Connections in Machinery
There are several alternatives to elastic couplings for achieving flexible connections in machinery:
1. Universal Joints: Universal joints, also known as U-joints, are mechanical devices that allow rotational motion between two shafts at different angles. They are suitable for applications with significant misalignment.
2. Cardan Shafts: Cardan shafts consist of a series of universal joints connected in a line, allowing for the transmission of torque and rotation in complex systems.
3. Oldham Couplings: Oldham couplings use sliding disks to transmit torque while accommodating small misalignments. They are suitable for applications where precise positioning is required.
4. Beam Couplings: Beam couplings use a flexible beam to transmit torque and compensate for angular and axial misalignment.
5. Diaphragm Couplings: Diaphragm couplings use thin diaphragms to transmit torque while compensating for misalignment. They are often used in high-performance applications.
6. Gear Couplings: Gear couplings use teethed gears to transmit torque and accommodate misalignment. They are suitable for heavy-duty applications.
7. Chain Couplings: Chain couplings use roller chains to transmit torque and handle misalignment. They are commonly used in low-speed, high-torque applications.
8. Bellows Couplings: Bellows couplings use a bellows-like flexible element to transmit torque while compensating for misalignment.
Each of these alternatives has its own advantages and limitations, and the choice depends on the specific requirements of the application.
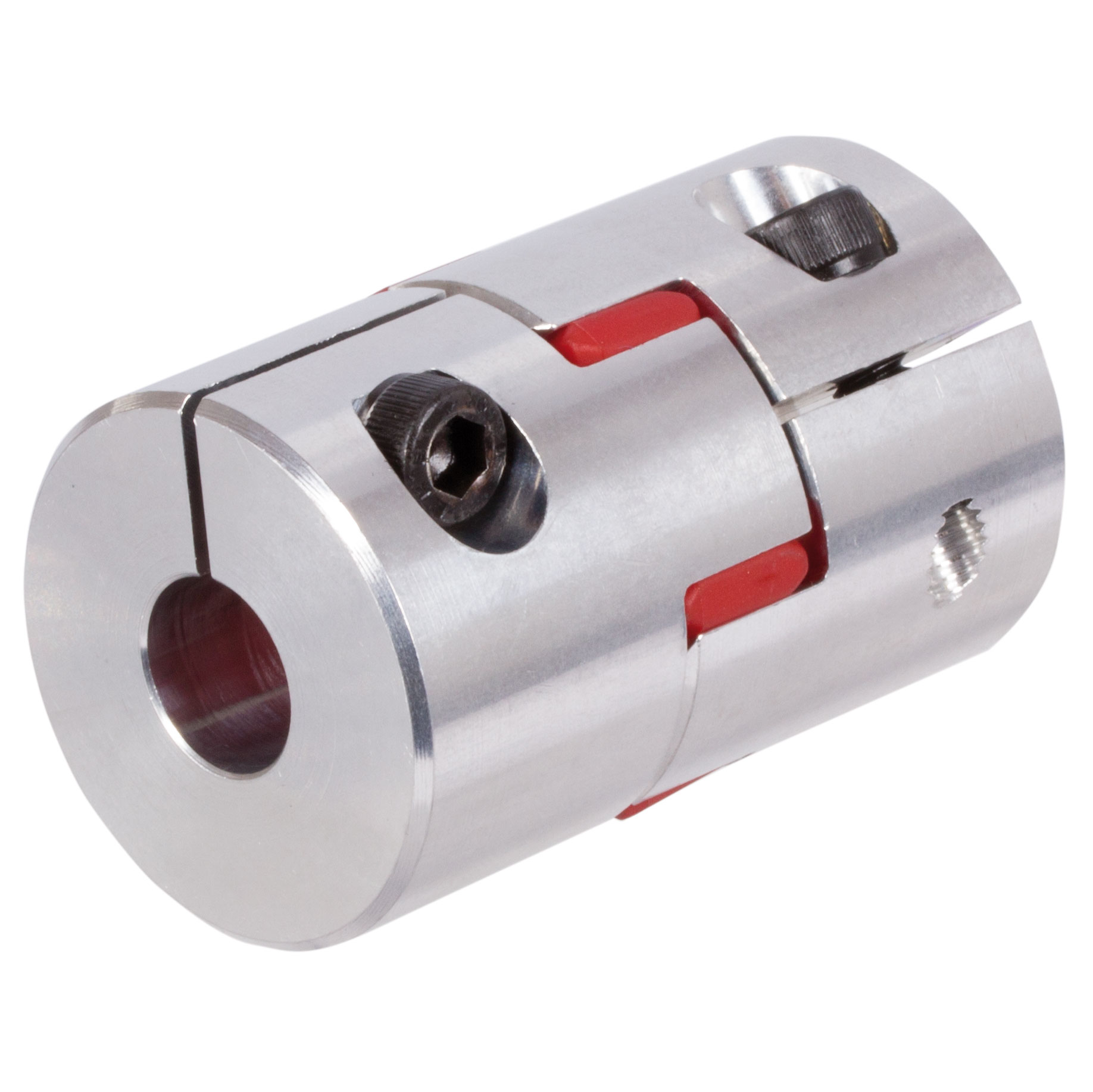

Principles of Torsionally Elastic Couplings
Torsionally elastic couplings, also known as flexible couplings, operate based on the principles of flexibility and torsional elasticity. These couplings are designed to transmit torque while accommodating misalignments, dampening vibrations, and providing protection against shock loads. Here’s how they work:
- Flexibility: Torsionally elastic couplings are made of materials that can flex or bend to some degree. This flexibility allows them to absorb misalignments between connected shafts, such as angular, parallel, and axial misalignments.
- Torsional Elasticity: The material properties of the coupling allow it to twist or deform slightly under torque loads. When torque is applied to one end of the coupling, the coupling flexes and twists to transmit torque to the other end while compensating for any misalignments.
- Vibration Dampening: The torsional elasticity of the coupling helps dampen vibrations that occur due to sudden torque changes or variations in load. This is especially important in applications where smooth operation and reduced vibrations are essential.
- Shock Load Protection: Torsionally elastic couplings can absorb and mitigate shock loads that might occur during sudden starts, stops, or changes in load. This protection prevents damage to connected equipment and extends the lifespan of machinery.
Overall, torsionally elastic couplings enhance the performance, reliability, and durability of machinery by providing flexibility, dampening vibrations, and protecting against misalignments and shock loads.


editor by CX 2024-04-29
China Custom CNC Aluminum Elastic Rubber Spider Jaw Shaft Coupler GF14*22 20*25 25*30 40*50 Shaft Flexible Coupling Ball Screw Plum Coupling
Product Description
Product Description
Coupling Deatails
Name: High precision plum blossom
coupling Model: LM-Material: Aviation Aluminum Alloy
Working temperature: -40 ° C ~ 100 ° C
Support customization: Factory direct sales support customization.
Features:
1.Intermediate Elastomer Connection-Absorbs vibration, compensates for radial, angular, and axial 2.misalignment
3.Oil resistance and electrical insulation
4.Clockwise and counterclockwise rotation characteristics are identical-there are 3 different hardness 5.elastomer
6.Fixation by clamping screw.
|
Model parameter |
ΦD |
L |
LF |
LP |
F |
M |
Tightening screw torque |
|
(N.M) |
|||||||
|
GF-14X22 |
14 |
22 |
14.3 |
6.6 |
3.8 |
M 3 |
0.7 |
|
GF-20X25 |
20 |
25 |
16.7 |
8.6 |
4 |
M 3 |
0.7 |
|
GF-20X30 |
20 |
30 |
19.25 |
8.6 |
5.3 |
M 4 |
1.7 |
|
GF-25X30 |
25 |
30 |
20.82 |
11.6 |
5.6 |
M 4 |
1.7 |
|
GF-25X34 |
25 |
34 |
22.82 |
11.6 |
5.6 |
M 4 |
1.7 |
|
GF-30X35 |
30 |
35 |
23 |
11.5 |
5.75 |
M 4 |
1.7 |
|
GF-30X40 |
30 |
40 |
25.6 |
11.5 |
10 |
M 4 |
1.7 |
|
GF-40X50 |
40 |
50 |
32.1 |
14.5 |
10 |
M 5 |
4 |
|
GF-40X55 |
40 |
55 |
34.5 |
14.5 |
10 |
M 5 |
4 |
|
GF-40X66 |
40 |
66 |
40 |
14.5 |
12.75 |
M 5 |
4 |
|
GF-55X49 |
55 |
49 |
32 |
16.1 |
13.5 |
M 6 |
8.4 |
|
GF-55X78 |
55 |
78 |
46.4 |
16.1 |
15.5 |
M 6 |
8.4 |
|
GF-65X80 |
65 |
80 |
48.5 |
17.3 |
18.1 |
M 8 |
10.5 |
|
GF-65X90 |
65 |
90 |
53.5 |
17.3 |
18.1 |
M 8 |
10.5 |
Product Parameters
Detailed Photos
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

Maintenance Requirements for Optimal Performance of Elastic Couplings
Maintaining elastic couplings is essential to ensure their optimal performance and longevity. Following these maintenance guidelines can help prevent premature wear and failure:
- Regular Inspection: Periodically inspect the coupling for signs of wear, such as cracks, deformities, or visible damage. This can help identify issues early and prevent further damage.
- Lubrication: Some elastic couplings require lubrication to reduce friction and wear. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for lubrication intervals and use compatible lubricants.
- Torque Check: Check the coupling’s torque values to ensure they are within the specified range. This helps maintain proper torque transmission and prevents overloading.
- Alignment Check: Monitor the alignment of the connected shafts regularly. Misalignment can cause excessive stress on the coupling, leading to premature failure.
- Vibration Analysis: Perform vibration analysis to identify any abnormal vibrations in the system. Excessive vibrations could indicate coupling or system issues that need attention.
- Temperature and Environment: Ensure that the coupling operates within the recommended temperature and environmental limits. Extreme conditions can affect the coupling’s material properties and performance.
- Coupling Wear: Keep track of the coupling’s wear over time. Depending on the application, the coupling might need replacement after a certain period of service.
- Expert Inspection: If any unusual symptoms or problems arise, consider having the coupling inspected by a qualified technician or engineer to diagnose the issue accurately.
Adhering to these maintenance practices helps extend the service life of elastic couplings, ensures reliable performance, and minimizes unexpected downtime and costly repairs.

Backlash in Elastic Couplings
Backlash refers to the amount of play or clearance between mating components in a mechanical system, particularly in elastic couplings. In an elastic coupling, backlash is the angular movement or rotation that occurs when there is a change in direction of the input shaft without an immediate response from the output shaft.
Backlash is a result of the elasticity and flexibility of the coupling’s components, such as the elastomer or other flexible elements. When the input direction changes, the elastic elements need to overcome their deformation before transmitting torque to the output shaft. This delay can lead to a temporary loss of motion and reduced precision in positioning applications.
Backlash can have a negative impact on the accuracy, repeatability, and overall performance of a machinery system. It can result in positioning errors, reduced responsiveness, and even potential damage to the system. Therefore, minimizing backlash is crucial in applications that require high precision and responsiveness.
Engineers can address backlash in elastic couplings by selecting couplings with lower compliance, optimizing the design to minimize the flexibility of the coupling elements, and using additional components like anti-backlash devices or preloaded mechanisms.

Industries Using Elastic Couplings
Elastic couplings find extensive use in various industries due to their unique benefits:
- Industrial Manufacturing: Elastic couplings are widely used in manufacturing equipment, conveyors, and assembly lines to maintain smooth operation and reduce vibrations.
- Automotive: Automotive applications include engine components, powertrain systems, and vehicle suspension systems where flexibility and vibration dampening are crucial.
- Power Generation: Elastic couplings are used in power generation equipment such as generators, turbines, and pumps to absorb torsional vibrations and enhance efficiency.
- Aerospace: In aerospace applications, elastic couplings help dampen vibrations in critical components like aircraft engines and control systems.
- Renewable Energy: Wind turbines and solar tracking systems benefit from elastic couplings to accommodate misalignments and vibrations caused by changing wind conditions.
- Mining: Mining equipment such as crushers, conveyors, and screens utilize elastic couplings to handle varying loads and minimize shock loads.
- Marine: Elastic couplings are used in marine propulsion systems and ship equipment to manage torque fluctuations and reduce vibrations.
These industries rely on elastic couplings to enhance performance, extend machinery lifespan, and minimize downtime due to vibrations, misalignments, and shock loads.


editor by CX 2024-04-22
China Standard CNC Aluminum Elastic Rubber Spider Jaw Shaft Coupler GF14*22 20*25 25*30 40*50 Shaft Flexible Coupling Ball Screw Plum Coupling
Product Description
Product Description
Coupling Deatails
Name: High precision plum blossom
coupling Model: LM-Material: Aviation Aluminum Alloy
Working temperature: -40 ° C ~ 100 ° C
Support customization: Factory direct sales support customization.
Features:
1.Intermediate Elastomer Connection-Absorbs vibration, compensates for radial, angular, and axial 2.misalignment
3.Oil resistance and electrical insulation
4.Clockwise and counterclockwise rotation characteristics are identical-there are 3 different hardness 5.elastomer
6.Fixation by clamping screw.
|
Model parameter |
ΦD |
L |
LF |
LP |
F |
M |
Tightening screw torque |
|
(N.M) |
|||||||
|
GF-14X22 |
14 |
22 |
14.3 |
6.6 |
3.8 |
M 3 |
0.7 |
|
GF-20X25 |
20 |
25 |
16.7 |
8.6 |
4 |
M 3 |
0.7 |
|
GF-20X30 |
20 |
30 |
19.25 |
8.6 |
5.3 |
M 4 |
1.7 |
|
GF-25X30 |
25 |
30 |
20.82 |
11.6 |
5.6 |
M 4 |
1.7 |
|
GF-25X34 |
25 |
34 |
22.82 |
11.6 |
5.6 |
M 4 |
1.7 |
|
GF-30X35 |
30 |
35 |
23 |
11.5 |
5.75 |
M 4 |
1.7 |
|
GF-30X40 |
30 |
40 |
25.6 |
11.5 |
10 |
M 4 |
1.7 |
|
GF-40X50 |
40 |
50 |
32.1 |
14.5 |
10 |
M 5 |
4 |
|
GF-40X55 |
40 |
55 |
34.5 |
14.5 |
10 |
M 5 |
4 |
|
GF-40X66 |
40 |
66 |
40 |
14.5 |
12.75 |
M 5 |
4 |
|
GF-55X49 |
55 |
49 |
32 |
16.1 |
13.5 |
M 6 |
8.4 |
|
GF-55X78 |
55 |
78 |
46.4 |
16.1 |
15.5 |
M 6 |
8.4 |
|
GF-65X80 |
65 |
80 |
48.5 |
17.3 |
18.1 |
M 8 |
10.5 |
|
GF-65X90 |
65 |
90 |
53.5 |
17.3 |
18.1 |
M 8 |
10.5 |
Product Parameters
Detailed Photos
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

Limitations and Disadvantages of Elastic Couplings
While elastic couplings offer various benefits, they also come with certain limitations and disadvantages that engineers and designers need to consider:
- Torsional Stiffness: Elastic couplings provide flexibility, but this can lead to lower torsional stiffness compared to rigid couplings. In applications requiring high torsional stiffness, elastic couplings might not be the ideal choice.
- Energy Loss: Due to the elastic nature of the material, a portion of the transmitted torque can be absorbed as deformation energy in the elastomer. This can result in energy losses and reduce overall efficiency.
- Wear and Fatigue: The elastomer element in elastic couplings can experience wear, fatigue, and deterioration over time, especially in applications with high loads or extreme operating conditions. Regular maintenance and monitoring are essential to ensure proper functionality.
- Temperature Sensitivity: Some elastomer materials used in elastic couplings might be sensitive to temperature fluctuations. Extreme temperatures can affect the properties of the elastomer and compromise the coupling’s performance.
- Alignment Requirements: While elastic couplings can accommodate minor misalignments, excessive misalignment can still lead to premature wear and reduced coupling lifespan. Proper alignment remains important for optimal performance.
Engineers and designers must carefully assess the specific requirements of their applications to determine if the advantages of elastic couplings outweigh the potential limitations and disadvantages.
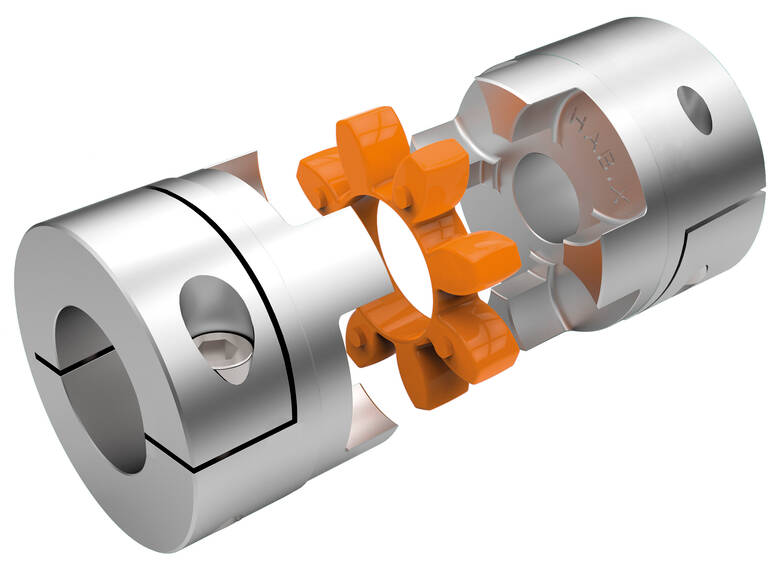
Maintaining the Longevity of Elastic Couplings
Ensuring the longevity and optimal performance of elastic couplings requires proper maintenance and care. Here are some key considerations:
- Regular Inspection: Periodically inspect the coupling for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Look for cracks, tears, or other deformations in the elastic elements.
- Lubrication: Some elastic couplings require lubrication for smooth operation. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines on lubrication intervals and recommended lubricants.
- Environmental Conditions: Consider the operating environment of the coupling. Extreme temperatures, chemicals, moisture, and other factors can affect the coupling’s lifespan. Choose materials and designs suitable for the specific conditions.
- Proper Alignment: Ensure that the connected components are properly aligned to minimize excessive stress on the coupling. Misalignment can accelerate wear and reduce performance.
- Load Capacity: Do not exceed the coupling’s recommended torque and load ratings. Overloading the coupling can lead to premature failure.
- Shock and Vibration: If the system experiences frequent shock or vibration, consider using dampening or vibration-absorbing components to reduce the stress on the coupling.
- Replacement: When signs of wear or damage become noticeable, promptly replace the coupling to avoid further issues. Delaying replacement can lead to more significant problems in the machinery system.
- Follow Manufacturer Guidelines: Always follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for installation, operation, and maintenance of the specific coupling model.
By adhering to these considerations and performing regular maintenance tasks, engineers can extend the lifespan of elastic couplings and ensure reliable and efficient operation in various machinery applications.

Factors to Consider When Selecting an Elastic Coupling
Engineers must carefully evaluate several factors when selecting an appropriate elastic coupling for a specific application. These factors ensure that the coupling can effectively meet the requirements of the machinery and system:
- Torque Transmission: Consider the amount of torque that needs to be transmitted between the connected shafts. Ensure that the coupling’s torque rating matches or exceeds the application’s torque requirements.
- Misalignment Compensation: Evaluate the expected misalignments between the shafts, such as angular, parallel, and axial misalignments. Choose a coupling with the appropriate flexibility and misalignment capacity to accommodate these variations.
- Vibration Dampening: Determine the level of vibration present in the system and select a coupling with the necessary torsional elasticity to dampen vibrations and provide smoother operation.
- Operating Speed: Consider the rotational speed of the connected shafts. Some elastic couplings may have speed limitations, so choose a coupling that can handle the desired operating speed without issues.
- Environmental Conditions: Assess the operating environment, including temperature, humidity, and the presence of contaminants. Choose a coupling material that can withstand the conditions and resist corrosion or degradation.
- Space Limitations: Take into account the available space for installing the coupling. Some couplings may have compact designs that are better suited for confined spaces.
- Shaft Sizes: Ensure that the coupling is compatible with the diameters of the connected shafts. Verify the coupling’s bore sizes and choose one that matches the shaft sizes.
- Installation and Maintenance: Consider the ease of installation and maintenance. Some couplings have simpler installation procedures, while others might require more complex procedures.
- Cost: Evaluate the budget for the coupling. While high-performance couplings might have added benefits, they could also come at a higher cost. Balance the performance requirements with budget constraints.
By carefully assessing these factors and selecting the appropriate elastic coupling, engineers can ensure optimal performance, longevity, and reliability of the machinery and systems they design.


editor by CX 2024-04-13
China Standard CNC Aluminum Elastic Rubber Spider Jaw Shaft Coupler GF14*22 20*25 25*30 40*50 Shaft Flexible Coupling Ball Screw Plum Coupling
Product Description
Product Description
Coupling Deatails
Name: High precision plum blossom
coupling Model: LM-Material: Aviation Aluminum Alloy
Working temperature: -40 ° C ~ 100 ° C
Support customization: Factory direct sales support customization.
Features:
1.Intermediate Elastomer Connection-Absorbs vibration, compensates for radial, angular, and axial 2.misalignment
3.Oil resistance and electrical insulation
4.Clockwise and counterclockwise rotation characteristics are identical-there are 3 different hardness 5.elastomer
6.Fixation by clamping screw.
|
Model parameter |
ΦD |
L |
LF |
LP |
F |
M |
Tightening screw torque |
|
(N.M) |
|||||||
|
GF-14X22 |
14 |
22 |
14.3 |
6.6 |
3.8 |
M 3 |
0.7 |
|
GF-20X25 |
20 |
25 |
16.7 |
8.6 |
4 |
M 3 |
0.7 |
|
GF-20X30 |
20 |
30 |
19.25 |
8.6 |
5.3 |
M 4 |
1.7 |
|
GF-25X30 |
25 |
30 |
20.82 |
11.6 |
5.6 |
M 4 |
1.7 |
|
GF-25X34 |
25 |
34 |
22.82 |
11.6 |
5.6 |
M 4 |
1.7 |
|
GF-30X35 |
30 |
35 |
23 |
11.5 |
5.75 |
M 4 |
1.7 |
|
GF-30X40 |
30 |
40 |
25.6 |
11.5 |
10 |
M 4 |
1.7 |
|
GF-40X50 |
40 |
50 |
32.1 |
14.5 |
10 |
M 5 |
4 |
|
GF-40X55 |
40 |
55 |
34.5 |
14.5 |
10 |
M 5 |
4 |
|
GF-40X66 |
40 |
66 |
40 |
14.5 |
12.75 |
M 5 |
4 |
|
GF-55X49 |
55 |
49 |
32 |
16.1 |
13.5 |
M 6 |
8.4 |
|
GF-55X78 |
55 |
78 |
46.4 |
16.1 |
15.5 |
M 6 |
8.4 |
|
GF-65X80 |
65 |
80 |
48.5 |
17.3 |
18.1 |
M 8 |
10.5 |
|
GF-65X90 |
65 |
90 |
53.5 |
17.3 |
18.1 |
M 8 |
10.5 |
Product Parameters
Detailed Photos
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
Real-World Applications of Elastic Couplings
Elastic couplings find extensive use in various industries and applications where the reduction of vibration and shock is critical for performance, efficiency, and equipment longevity. Here are some examples:
- Industrial Machinery: Elastic couplings are commonly employed in industrial machinery such as pumps, compressors, conveyors, and generators. They help minimize vibration and shock, ensuring smooth and reliable operation while protecting sensitive components.
- Automotive Industry: In automotive applications, elastic couplings are used in drivetrains to dampen vibrations and shocks between the engine and the transmission. This enhances driving comfort, reduces noise, and prevents excessive wear on connected components.
- Power Generation: Power generation equipment, including turbines and generators, benefits from elastic couplings that absorb torsional vibrations and shocks. This aids in maintaining stable power output and extending the lifespan of critical components.
- Printing and Packaging: Printing presses and packaging machinery rely on elastic couplings to reduce vibrations during high-speed operations. This ensures precise printing and packaging while preventing damage to sensitive components.
- Robotics and Automation: Elastic couplings are crucial in robotics and automation systems to mitigate vibrations and shocks that can affect accuracy and reliability. They enable precise movement control and consistent performance.
- Medical Equipment: Medical devices such as MRI machines and X-ray equipment utilize elastic couplings to minimize vibrations that could impact image quality and precision during medical procedures.
These examples highlight how elastic couplings contribute to optimal performance, reduced maintenance, and increased equipment lifespan across diverse industries.

Alternatives to Elastic Couplings for Flexible Connections in Machinery
There are several alternatives to elastic couplings for achieving flexible connections in machinery:
1. Universal Joints: Universal joints, also known as U-joints, are mechanical devices that allow rotational motion between two shafts at different angles. They are suitable for applications with significant misalignment.
2. Cardan Shafts: Cardan shafts consist of a series of universal joints connected in a line, allowing for the transmission of torque and rotation in complex systems.
3. Oldham Couplings: Oldham couplings use sliding disks to transmit torque while accommodating small misalignments. They are suitable for applications where precise positioning is required.
4. Beam Couplings: Beam couplings use a flexible beam to transmit torque and compensate for angular and axial misalignment.
5. Diaphragm Couplings: Diaphragm couplings use thin diaphragms to transmit torque while compensating for misalignment. They are often used in high-performance applications.
6. Gear Couplings: Gear couplings use teethed gears to transmit torque and accommodate misalignment. They are suitable for heavy-duty applications.
7. Chain Couplings: Chain couplings use roller chains to transmit torque and handle misalignment. They are commonly used in low-speed, high-torque applications.
8. Bellows Couplings: Bellows couplings use a bellows-like flexible element to transmit torque while compensating for misalignment.
Each of these alternatives has its own advantages and limitations, and the choice depends on the specific requirements of the application.
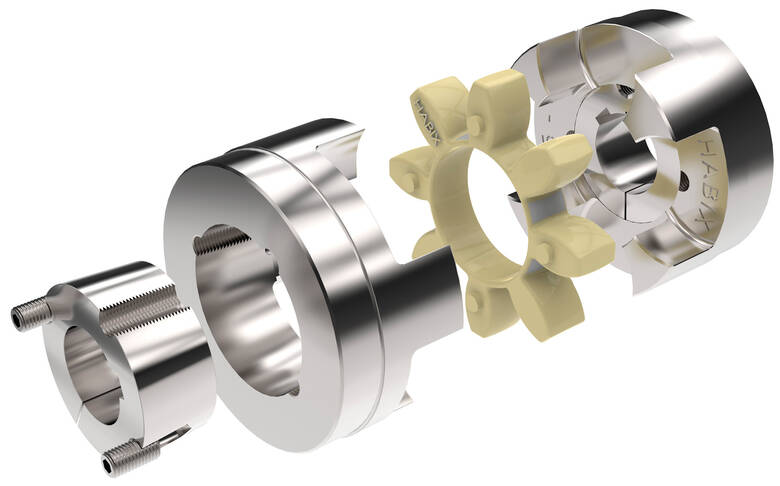

Types of Elastic Couplings for Specific Applications
There are various types of elastic couplings available, each designed to suit specific industrial applications:
- Flexible Jaw Couplings: These couplings use an elastomeric element to transmit torque and accommodate misalignment. They are commonly used in applications where shock absorption and vibration damping are important, such as pumps, compressors, and conveyor systems.
- Diaphragm Couplings: Diaphragm couplings use thin metal diaphragms to transmit torque while allowing for angular, axial, and radial misalignment. They are often used in high-performance applications where precise motion transmission is required, such as in robotics, precision machinery, and aerospace systems.
- Torsional Couplings: Torsional couplings are designed to handle high torque loads and are commonly used in heavy-duty applications, including industrial machinery, mining equipment, and large pumps.
- Disc Couplings: Disc couplings use multiple thin metal discs to transmit torque and accommodate misalignment. They are suitable for applications requiring high torque transmission and precise motion control, such as turbines, generators, and high-speed machinery.
- Beam Couplings: Beam couplings use helical cuts in a flexible beam to provide torsional flexibility and misalignment compensation. They are used in applications that require moderate torque transmission and misalignment accommodation, such as stepper motors and motion control systems.
- Oldham Couplings: Oldham couplings use three disks to transmit torque while allowing for axial misalignment. They are commonly used in applications that require accurate motion transmission, such as linear actuators and CNC machinery.
The choice of the right type of elastic coupling depends on factors such as the application’s torque requirements, speed, misalignment characteristics, and specific performance needs.


editor by CX 2024-04-03
China Custom CNC Aluminum Elastic Rubber Spider Jaw Shaft Coupler GF14*22 20*25 25*30 40*50 Shaft Flexible Coupling Ball Screw Plum Coupling
Product Description
Product Description
Coupling Deatails
Name: High precision plum blossom
coupling Model: LM-Material: Aviation Aluminum Alloy
Working temperature: -40 ° C ~ 100 ° C
Support customization: Factory direct sales support customization.
Features:
1.Intermediate Elastomer Connection-Absorbs vibration, compensates for radial, angular, and axial 2.misalignment
3.Oil resistance and electrical insulation
4.Clockwise and counterclockwise rotation characteristics are identical-there are 3 different hardness 5.elastomer
6.Fixation by clamping screw.
|
Model parameter |
ΦD |
L |
LF |
LP |
F |
M |
Tightening screw torque |
|
(N.M) |
|||||||
|
GF-14X22 |
14 |
22 |
14.3 |
6.6 |
3.8 |
M 3 |
0.7 |
|
GF-20X25 |
20 |
25 |
16.7 |
8.6 |
4 |
M 3 |
0.7 |
|
GF-20X30 |
20 |
30 |
19.25 |
8.6 |
5.3 |
M 4 |
1.7 |
|
GF-25X30 |
25 |
30 |
20.82 |
11.6 |
5.6 |
M 4 |
1.7 |
|
GF-25X34 |
25 |
34 |
22.82 |
11.6 |
5.6 |
M 4 |
1.7 |
|
GF-30X35 |
30 |
35 |
23 |
11.5 |
5.75 |
M 4 |
1.7 |
|
GF-30X40 |
30 |
40 |
25.6 |
11.5 |
10 |
M 4 |
1.7 |
|
GF-40X50 |
40 |
50 |
32.1 |
14.5 |
10 |
M 5 |
4 |
|
GF-40X55 |
40 |
55 |
34.5 |
14.5 |
10 |
M 5 |
4 |
|
GF-40X66 |
40 |
66 |
40 |
14.5 |
12.75 |
M 5 |
4 |
|
GF-55X49 |
55 |
49 |
32 |
16.1 |
13.5 |
M 6 |
8.4 |
|
GF-55X78 |
55 |
78 |
46.4 |
16.1 |
15.5 |
M 6 |
8.4 |
|
GF-65X80 |
65 |
80 |
48.5 |
17.3 |
18.1 |
M 8 |
10.5 |
|
GF-65X90 |
65 |
90 |
53.5 |
17.3 |
18.1 |
M 8 |
10.5 |
Product Parameters
Detailed Photos
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

Material Selection and Design Durability of Elastic Couplings
The choice of materials for elastic couplings significantly influences their design and overall durability. Material selection affects factors such as flexibility, torsional stiffness, fatigue resistance, and resistance to environmental conditions. Here’s how material selection plays a crucial role:
- Elastomer Material: The elastomer used in elastic couplings determines the coupling’s flexibility, vibration absorption capabilities, and resilience. Common elastomers include natural rubber, synthetic rubber, and polyurethane. The selected elastomer should provide the desired level of elasticity and durability while maintaining its properties over time.
- Hub and Spacer Material: The hubs and spacers of elastic couplings are typically made from metals like steel, aluminum, or alloy materials. These components need to be strong enough to transmit torque while accommodating misalignments and vibrations. The material should also resist wear, corrosion, and fatigue.
- Bolt or Pin Material: Bolts or pins used to connect the hubs and elastomer element must possess sufficient strength to handle the torsional forces and loads. They should be made from materials with high tensile strength and corrosion resistance.
- Environmental Factors: Depending on the application environment, material selection should consider factors such as temperature, moisture, chemicals, and UV exposure. The chosen materials should be able to withstand these conditions without deterioration.
Ultimately, a well-considered material selection enhances the coupling’s durability, operational performance, and resistance to wear, ensuring that the elastic coupling can reliably function under varying conditions and loads.

Impact of Temperature Variations on Elastic Coupling Performance
Elastic couplings can be sensitive to temperature variations, and their performance can be influenced by both high and low temperatures:
1. High Temperatures: Elevated temperatures can cause the elastomeric material used in elastic couplings to soften, leading to a decrease in its mechanical properties. This can result in reduced torsional stiffness, damping capabilities, and overall coupling performance. High temperatures can also accelerate the aging process of the elastomer, leading to a shorter lifespan of the coupling. Additionally, excessive heat can cause thermal expansion of the coupling’s components, potentially leading to misalignment issues.
2. Low Temperatures: Extremely low temperatures can cause the elastomeric material to become more rigid, reducing its flexibility and damping characteristics. This can result in increased transmission of vibrations and shocks between connected components. Cold temperatures can also make the elastomer more brittle, increasing the risk of cracking or rupturing under mechanical stress.
It’s important to select an elastic coupling material that is suitable for the anticipated temperature range of the application. Some elastomers are formulated to perform well across a wide temperature range, while others are better suited for specific temperature conditions. Regular maintenance and inspection of elastic couplings in extreme temperature environments are crucial to ensure that the coupling continues to function as intended.

Difference Between Elastic Coupling and Rigid Coupling
Elastic couplings and rigid couplings are two distinct types of couplings used in mechanical designs:
Elastic Coupling: An elastic coupling incorporates an elastomeric material, such as rubber, to provide flexibility and absorb shock and vibration. It allows for misalignment compensation and is ideal for applications where there may be slight misalignment or the need for vibration damping. Elastic couplings are commonly used in machinery that requires smooth operation and reduced stress on connected components.
Rigid Coupling: A rigid coupling, as the name suggests, is designed to provide a solid connection between two shafts. It does not have any flexible or damping elements and is used when precise alignment and torque transmission are critical. Rigid couplings are often used in applications where shafts need to maintain a constant alignment, such as in precision machines and systems with high torque requirements.
The choice between an elastic coupling and a rigid coupling depends on the specific requirements of the mechanical system, including the degree of misalignment, vibration levels, torque transmission, and the overall performance objectives.


editor by CX 2024-04-03